Chapter XIX
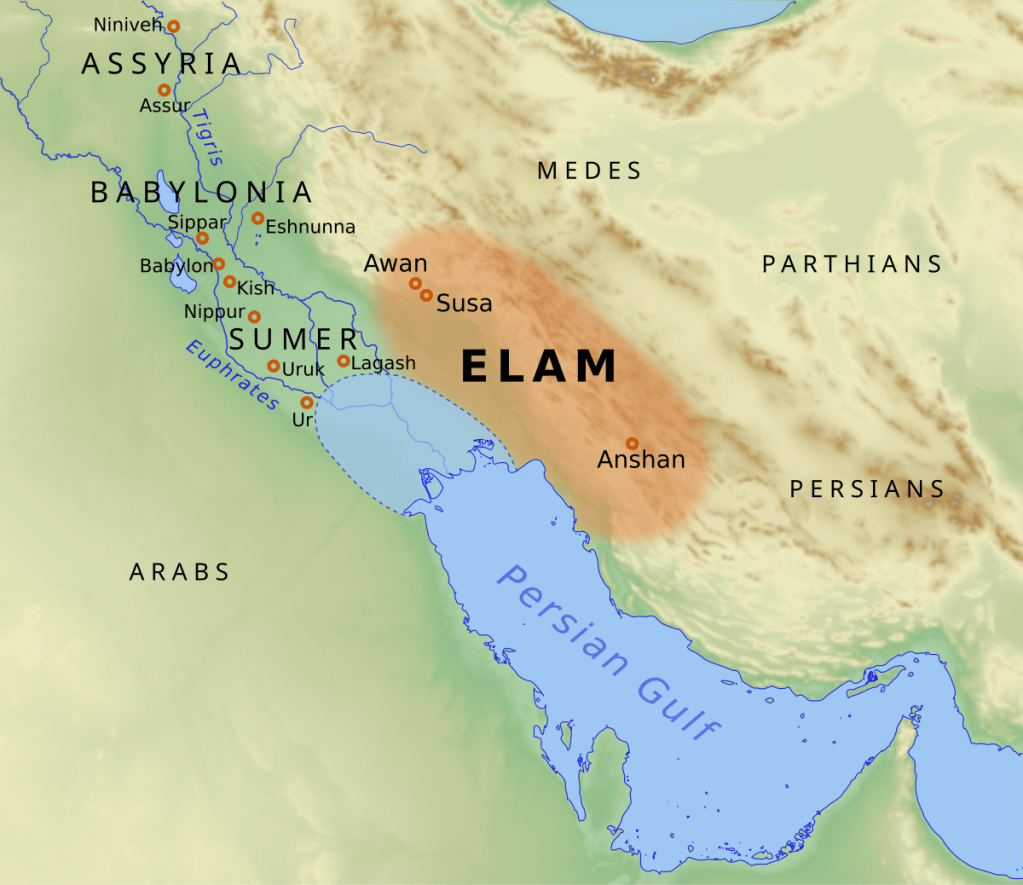
The earliest known historical figure connected with Elam, is Enmebaragsei, the penultimate king of the first Dynasty of Kish who reigned over much of Sumer, possibly as late as circa 2615 to 2600 BCE. The Sumerian King List says he reigned nine hundred years. A more realistic 15 years is probable when dividing by 60, based on the Sumerian sexagesimal system according to an unconventional chronology. Enmebaragesi is a key figure as he bridges the divide between myth and history. He is the earliest ruler to be evidenced directly from archaeology. Four inscriptions have been found with his name. En is an honorary title and not part of his original name. Me means crown; bara means ruler; and si means to fill.
Enmebaragsei fought a successful campaign against Elam, capturing Uruk, confiscating their weapons and imposing his kingship – he “who made the land of Elam submit.” He preceded the Old Elamite period dated to circa 2600 to 1500 BCE, broadly incorporating three main dynasties beginning from approximately the end of his reign. They were the combined Awan I and II era, circa 2600 to 2300 BCE and 2300 to 1930 BCE consecutively; the Shimashki (or Simaski) era, circa 1955 to 1840 BCE; and the Sukkalmah era, circa 1840 to 1500 BCE. It is the end of the 1st dynasty and the beginning of the 2nd with which we are primarily interested.
The Awan (or Avan) II dynasty was contemporary with the Mesopotamian emperor Sargon I or the Great of Akkad, reigning from 2224 to 2169 BCE. He defeated the 12th Awan king, Luh-Ishshan – who reigned circa 2194 to 2169 BCE – subjugating Susa. Historical sources concerning Elam now become more frequent, as the Mesopotamians had developed an interest in resources, such as wood, stone and metal from the Iranian plateau; thereby encouraging more frequent military excursions to the region.
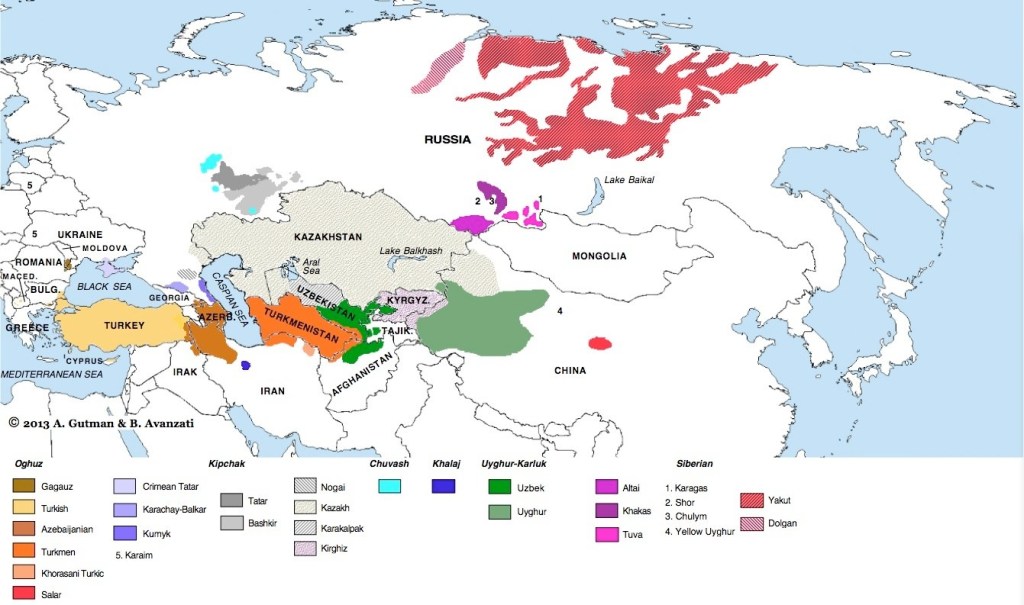
Though the foreign Guti Dynasty (refer Chapter XXIII Aram & Tyre: Spain, Portugal & Brazil) had been ruling in Sumer since 2088 BCE, it was in 2039 BCE that Akkad fell to the Gutians and with it, the final and 11th king of the Dynasty of Akkad – Shu-Dural (or Shu-Tural). The Gutium spoke an agglutinative language isolate like Sumer and Elam – refer Chapter XXIV Arphaxad & Joktan: Balts, Slavs & the Balkans; and Chapter XVIII Elam & Turkey.
The Gutians ruled Sumer and Elam until 1991 BCE. The last king of nineteen, Tirigan, reigned for only 40 days, when Utu-hengal reigning from 1995 to 1988 BCE of the 5th Dynasty of Uruk defeated him – ending the Gutian Dynasty.
Now, Utu-Hengal was the father of Ur-Namma the 1st King of the Ur III Dynasty from 1988 to 1970 BCE and he in turn, was the father of King Shulgi who reigned from 1970 to 1924 BCE.
These names are mentioned as there is considerably more to say about Ur-Namma as we progress, who was concurrent with King Kutik-Inshushinak of Elam the next to last king before Chedorlaomer; as well as Shulgi, the 2nd King of Ur, who was a contemporary of the Elamite King Chedorlaomer, as well as the Patriarch Abraham.
Elam declared independence under the supposedly last and 17th Awan king, Kutik-Inshushinak (or Puzur-Insusinak) who reigned from 1980 to 1955 BCE, throwing off the Akkadian language and promoting the Linear Elamite script in the process. Kutik-Inshushinak conquered the future principal Elamite cities of Susa and Anshan. The Shimashki dynasty arose at the tail end of the Awan Dynasties, with an unnamed king from 1955 to 1930 BCE, so that there was a crossover of some twenty-five years. Elam endured a continual threat of attacks from the Sumerians and the Gutians. The Elamite empire state of Shimashki at this time extended into northern Iran and as far as the Caspian Sea.
A century later in 1882 BCE, the Elamites allied with the city of Susa and led by their king Kindattu (or Kindadu) – ruler from 1892 to 1872 BCE – the 10th king of the Shimashki Dynasty, sacked Ur in Sumer with the first Akkadian King of Isin (or Issn), Ishbi-Erra from 1895 to 1862 BCE; and defeated the 5th and final king of the Ur III Dynasty, the great grandson of Shulgi: Ibbi-Suen, who reigned twenty-four years beginning in 1906 BCE.
The succeeding Sukkalmah dynasty lasting from 1840 to 1500 BCE, is so named after the ‘Great or Grand regents’, the title borne by Elamite rulers. It was also called the Epartid dynasty after the name of its founder Eparti II – also known as Ebarti (or Ebarat) who reigned from circa 1840 to 1820 BCE – and was concurrent with both the Old Assyrian Empire and the Old Babylon period in Mesopotamia. Eparti II was a contemporary of Iddin-Dagan and his reign from 1842 to 1822 BCE; the grandson of Ishbi-Erra and 3rd King of the Isin Dynasty in Akkad – marrying his daughter.
A ruler named Silhaha – (or Shilkhakha), ruling from 1820 to 1800 BCE – who described himself as ‘the chosen son of Ebarti’ is also credited as the founder of the dynasty. Ebarti II appears as the founder of the dynasty according to building inscriptions, but later kings refer to the second ruler Silhaha, Eparti’s son, in their filiation claims. Possibly, Silhaha won out over a brother; as there was an Eparti III before Shilhaha. Both their names as the founding members of the Sukkalmah Dynasty, have been found on the Gunagi silver vessels, inscribed in the Linear Elamite script. The Gunagi vessels were discovered only recently in 2004.
Notable Eparti dynasty rulers in Elam during this time include the 12th king Siruk-tuh (or Shirukduh), circa 1660 to 1640 BCE, who entered various military coalitions to contain the power of the southern Mesopotamian states; 14th ruler and a son of Siruk-tuh, Siwe-Palar-hupak, circa 1615 to 1595 BCE, who for some time was the most powerful ruler in the region, respectfully addressed as ‘Father’ by Mesopotamian kings such as Zimri-Lim of Mari.

The 16th king, Kutir-Nahhunte I (or Kedor-nakhunta), circa 1560 to 1530 BCE, exacted revenge and plundered the temples of southern Mesopotamia, as the North was under the control of the Old Assyrian Empire. In fact, Kutir-Nahhunte dealt so serious a defeat to the Babylonians that the event was remembered nearly one thousand years later in an inscription of the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal, when he conquered Susa in 660 BCE.
Trade between the Indus Valley Civilisation and the cities of Mesopotamia and Elam have been deduced from numerous Indus artefacts; particularly in excavations in Susa, showing the origination of the post-diluvian society in the east and the subsequent migration west to the plains of Mesopotamia – refer Chapter I Noah Antecessor Nulla.
Objects made with shell species that are characteristic of the Indus coast, such as Trubinella Pyrum and Fasciolaria Trapezium, have been found in the archaeological sites of Mesopotamia and Susa dated circa 2500 to 2000 BCE. Carnelian beads from the Indus were found in Susa in the tell of the citadel excavation. Exchanges seem to have waned after 1900 BCE, with the eventual demise of the Indus valley civilisation.
It is to this backdrop that we read of an extraordinary account in Genesis chapter fourteen. For a biblical account, it is remarkably detailed and it comprises two parts. A war between a confederacy of Southern Mesopotamian kings against vassal Canaanite kings to the southwest, which we will now look at and an amazing rescue operation of Lot by his uncle, the patriarch Abraham which we will study later in Chapter XXVII Abraham & Keturah – Benelux & Scandinavia.
Genesis 14:1-11
English Standard Version
1 ‘In the days of [1] Amraphel king of Shinar, [2] Arioch king of Ellasar, [3] Chedorlaomer king of Elam, and [4] Tidal king of Goiim [or Nations],
2 these kings made war with
Bera king of Sodom, Birsha king of Gomorrah, Shinab king of Admah, Shemeber king of Zeboiim, and the king of Bela (that is, Zoar).
3 And all these joined forces in the Valley of Siddim (that is, the Salt Sea) [north of the present day Dead Sea].
4 Twelve years [from 1907 to 1895 BCE] they had served Chedorlaomer, but in the thirteenth year they rebelled [1907-1895 BCE].
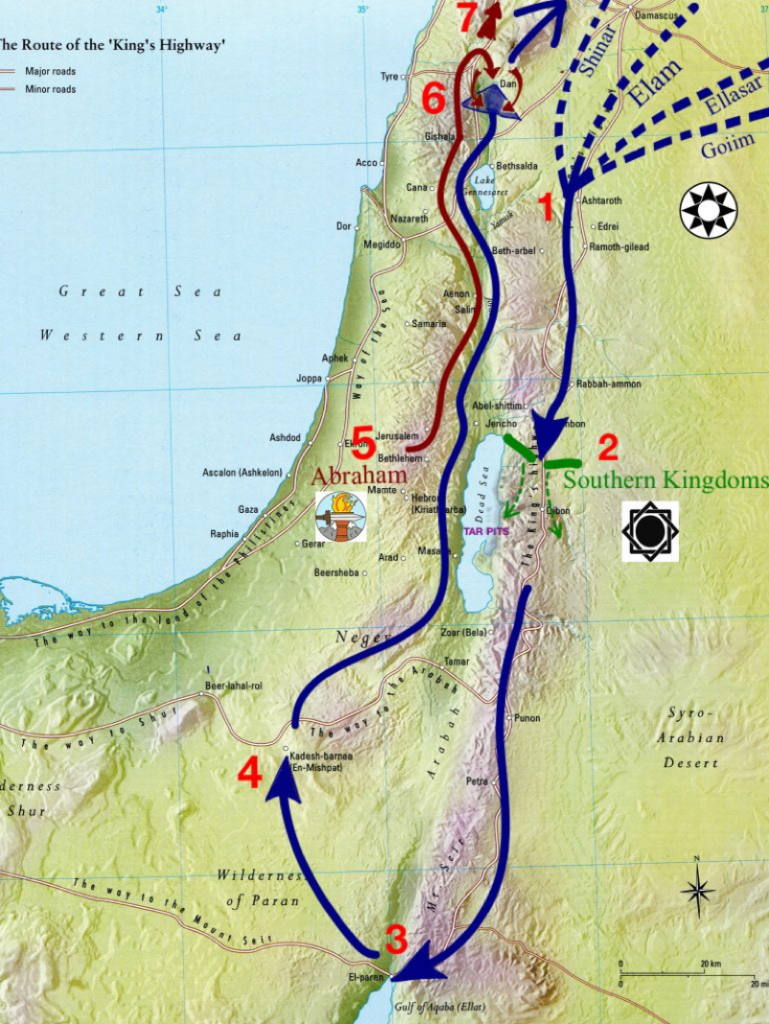
5 In the fourteenth year [1894 BCE] Chedorlaomer and the kings who were with him came and defeated the Rephaim in Ashteroth-karnaim, the Zuzim in Ham, the Emim in Shaveh-kiriathaim,
6 and the Horites in their hill country of Seir as far as El-paran on the border of the wilderness. 7 Then they turned back and came to En-mishpat (that is, Kadesh) and defeated all the country of the Amalekites, and also the Amorites who were dwelling in Hazazon-tamar.
8 Then the king of Sodom, the king of Gomorrah, the king of Admah, the king of Zeboiim, and the king of Bela (that is, Zoar) went out, and they joined battle in the Valley of Siddim 9 with [1] Chedorlaomer king of Elam, [2] Tidal king of Goiim, [3] Amraphel king of Shinar, and [4] Arioch king of Ellasar, four kings against five. 10 Now the Valley of Siddim was full of bitumen pits, and as the kings of Sodom and Gomorrah fled, some fell into them, and the rest fled to the hill country [of Seir].
11 So the enemy took all the possessions of Sodom and Gomorrah, and all their provisions, and went their way.’
The five kings of the Plain, happen to represent the exact same five cities that the angels of the Lord came to destroy, sixteen years later and in the process, dramatically rescue Abraham’s nephew Lot, for the second time in his life. The references to the Repha-im, Zuz-im and Em-im are all clans of Nephilim offspring. In fact, the Horites and Amalekites are also included with these mysterious tribes. We will discuss these peoples in depth, in Chapter XXII Alpha & Omega and in Chapter XXIX Esau: The thirteenth Tribe.
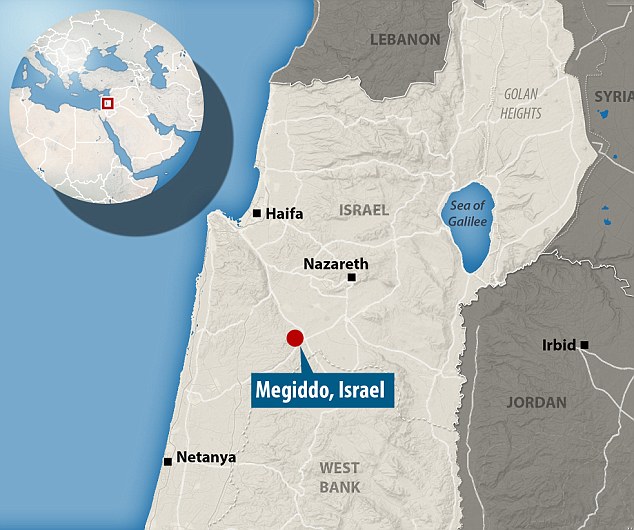
Though Chedorlaomer I of Elam is listed third – he is placed first in verse nine – Chedorlaomer is the leader of the northern confederacy. The only king not stated is that of Bela or Zoar. This city and its people were the only one of the five which were not destroyed by the Creator’s wrath during the time of Lot. The time frame is particularly critical, as this battle would need to have taken place between Abraham’s birth in 1977 BCE and his death in 1802 BCE. This would align with the end of the Awan II Dynasty and the beginning of the Shimashki.

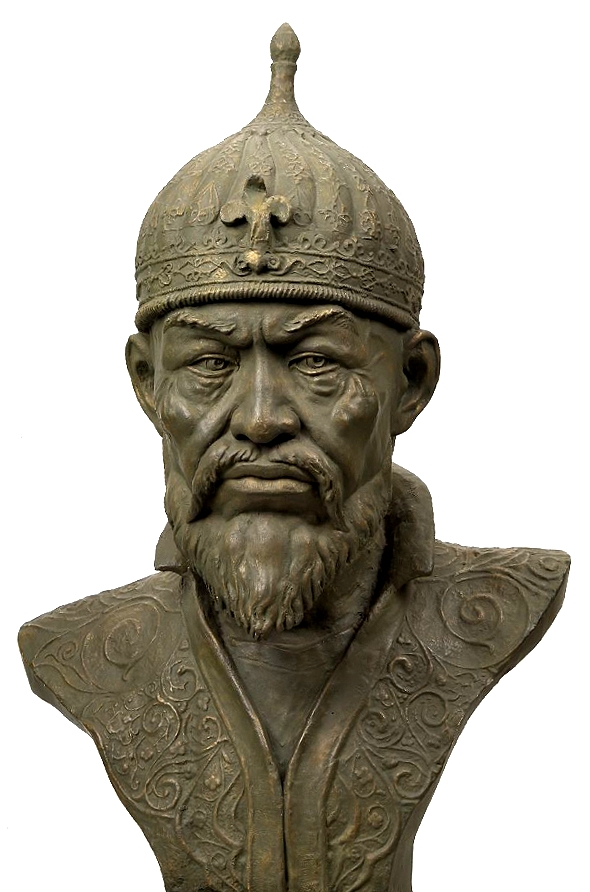
Head of Chedorlaomer (and no, it is not Tom Hanks): Height 34.3 cm in Arsenical Copper from Iran, circa 2000 BCE.
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 1947

Hitchcock’s Bible Names Dictionary defines the name Chedorlaomer as: a roundness of a sheaf; Smith’s Bible Dictionary as: a handful of sheaves. The full name Chedorlaomer, is not known outside the Bible, although the name is genuinely Elamite. It is composed of two elements, which do appear separately in Elamite sources. ‘Laomer’ is apparently a divine name whose Elamite form is Lagamar. ‘Chedor’ is derived from the Elamite Katir (orKutir), meaning ‘servant’. We have seen its use in the name of the 16th Sukkalmah Dynasty King Kutir-Nahhunte. The name could also mean ‘servant of the god Lagamar’.
Easton’s Bible Dictionary – emphasis & bold mine:
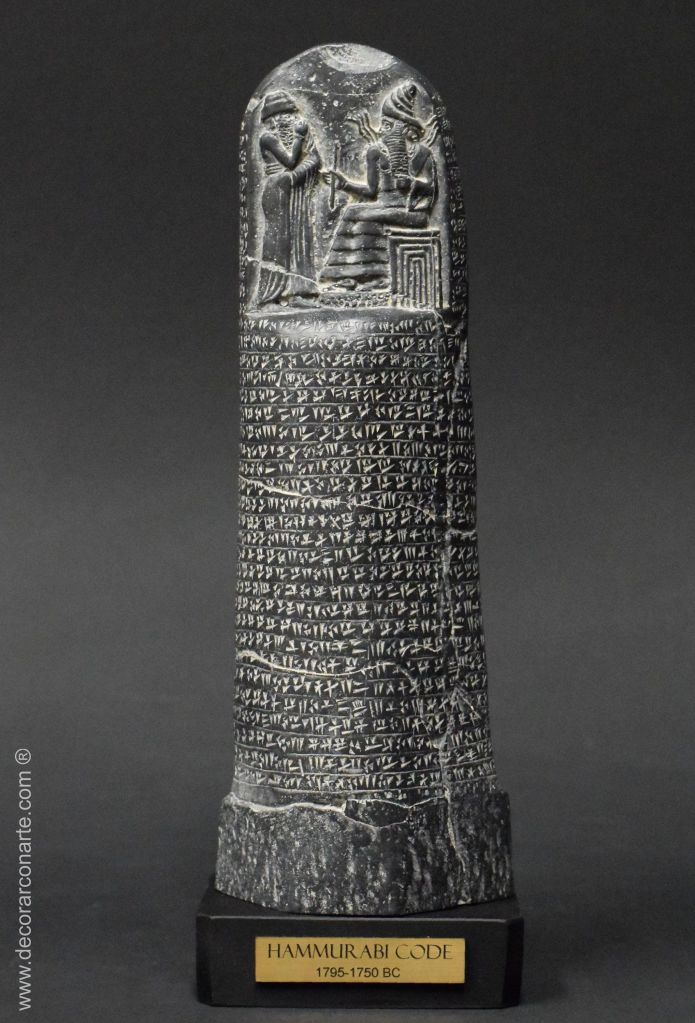
‘Many centuries before the age of Abraham, Canaan and even the Sinaitic peninsula had been conquered by Babylonian kings, and in the time of Abraham himself Babylonia was ruled by a dynasty which claimed sovereignty over Syria and Palestine. The most famous king of the dynasty was Khammu-rabi‘ (or Hammurabi), ‘who united Babylonia under one rule, and made Babylon its capital. When he ascended the throne’ – in 1894 BCE an unconventional chronology – ‘the country was under the suzerainty of the Elamites, and was divided into two kingdoms, that of Babylon (the Biblical Shinar) and that of Larsa (the Biblical Ellasar).
The king of Larsa was Eri-Aku (“the servant of the moon-god”), the son of an Elamite prince, Kudur-Mabug’ or Durmah-ilani, ‘who is entitled “the father of the land of the Amorites.” A recently discovered tablet enumerates among the enemies of Khammu-rabi, Kudur-Lagamar (“the servant of the goddess Lagamar”) or Chedorlaomer, Eri-Aku or Arioch, and Tudkhula or Tidal. Khammu-rabi, whose name is also read Ammi-rapaltuor [for] Amraphel by some scholars, succeeded in overcoming Eri-Aku and driving the Elamites out of Babylonia.’
After the Valley of Siddim campaign, Hammurabi – or Amraphel, King of Shinar and – King of Babylon, ironically chose to go against his three former allies and circa 1893 BCE, he too rebelled. As we progress, we will possess significant support for the confirmation of the four Northern kings identities as real historical figures, as well as a credible time frame for the events recorded. It is proposed that Hammurabi was born in 1912 BCE according to an unconventional chronology and ascended the Babylonian throne in 1894 BCE, at the age of 18; following the abdication of the 5th king of the Amorite Dynasty, his father Sin-Muballit, who ruled for nineteen years from 1913 BCE.
There is fevered debate over when Hammurabi of Babylon lived. This is convenient for scholars, in that it neatly throws a spanner in the works for conclusively supporting the accuracy of the biblical account. Hammurabi is a colourful and influential king in ancient history and thus for detractors, it is problematic to have such a clear sign of the authenticity of the biblical record; which in turn underpins the veracity of the existence of Abraham and his nephew Lot, whom both fathered peoples who have become prominent 21st century nations.
An informative paper: Abraham and Chedorlaomer Chronological, Historical and Archaeological Evidence by Gérard Gertoux; provides comprehensive research in presenting the evidence for Chedorlaomer’s identity and his place as a legitimate historical king. Where we firstly and slightly disagree, is in the chronology by sixty years; for he has presumably, dated the Exodus in the early sixteenth century, circa 1507 BCE as opposed to the middle of the fifteenth century in 1446 BCE. Secondly, he has adopted the most recent academic opinion regarding the time frame for Hammurabi’s rule; some 200 to 150 years later than proposed here – Appendix IV: An Unconventional Chronology.
He states, emphasis & bold mine:
‘The only way to assess the veracity (historical truth) of this event is by determining its exact chronology (“the backbone of history”). Foremost one should know that until now Babylonian chronology, which is the best known, has not been yet fixed since Oppert (1863) made the start of the reign of Hammurabi in 2394 BCE, Thureau-Dangin (1927) lowered this date to 2003 BCE and Gasche proposed (1998) lowering it again to 1696 BCE. Hammurabi has rejuvenated about 700 years during the 20th century!
When T.G. Pinches (1856-1934), lecturer in Assyriology at University College, London and at the University of Liverpool, published the Spartoli tablets he made a link between the biblical names:
Amraphel, Arioch, Chedorlaomer and Tidal (Genesis 14:1) and Hammurabi, Eri-e-Aku, Kudur-lahgamal and Tudḫula.
Unfortunately this deduction has three major errors: 1) Hammurabi (1697-1654) reigned three centuries after the events, 2) his name is very different from that of Amraphel and 3) the reading “laḫ” of the sign KU [for Chedorlaomer] is not documented.’
These three reasons are flimsy at best and are really no more than excuses. The dating conflict regarding Hammurabi’s timeline, means it has to be reconciled with other documents to understand when he truly lived. As we will find that Hammurabi was indeed a contemporary of Chedorlaomer, Arioch and Tidal, it is fitting to parallel his timeline with them. This then resolves the dates for Hammurabi’s life.
Some scholars have made the connecting link between the names Hammurabi and Amraphel. That aside, it is not unusual for people and places to have more than one name. Amraphel may have been his given name. As he was only eighteen when he ascended the Babylonian throne after Sin-Muballit and then ruled for a lengthy forty-two years. A new name may have been chosen as monarchs have done up until our recent history. The Bible possibly records his name as Amraphel as he had just ascended the throne and was in his very first year of his reign. An accurate record, no less than his being subsequently known after his exploits as Hammurabi and recorded as such in future histories.
Etymology shows the lah is actually part of Chedorlaomer’s name, though regardless, the Kudur-…gamal is still strong evidence for the correlation with his identity. Gertoux mixes Akkadian and Elamite together, to show the kudur is Akkadian and la(h)gamal is Elamite. The Akkadian actually says: kudur-lagamar and the Elamite says: kutir-lagamol. The Greek Septuagint refers to him as Chodol-logomor and it is synonymous with the aforementioned as well as the Hebrew name: Kdorla’omer.
Gérard Gertoux – emphasis & bold mine:
‘Ku-du7-[ur-La-ga-mar] (line 13) reigned 36 years (line 14) over Akkad as king of Awan I (Elam). King List WB 444 (Weld-Blundell Prism) dated c. 1800 B.C. Ashmolean Museum, Oxford (number: AN1923.44).
Kudur-Lagamar’s name is located in a part of the prism which is unfortunately very damaged but three important data have been preserved: [1] a mighty king of Elam at the end of the 3rd millennium BCE, [2] whose name was Kudu[-], [3] died without a successor.
A chronological reconstruction based on synchronisms shows that among the dynasties from Sumerian lists the third and last Elamite king of the Awan I dynasty was Kudur-Lagamar.’

‘The three Elamite kings of the dynasty of Awan I (Puzur-Insusinak [Kutik-Insusinak 1980-1955 BCE], [-]-lu [1955-1930 BCE], Kudur-Lagamar [1929-1893 BCE]) were regarded as genuine kings of Akkad in parallel with the Sumerian kings of the dynasty of Ur III (Ur-Nammu, Sulgi). Besides they used Akkadian in their writings, in place of Elamite, and they quoted Mesopotamian gods rather than their Elamite divinities.’
The Northern kings listed in Genesis fourteen verse one could be geographical in orientation, as Larsa is south of Babylon and Elam is south of Ellasar. Some researchers believe Tidal, King of Nations refers to a very northwesterly position and the peoples of Hatti, or later the Hittites in Anatolia. This would not fit with the cluster of powers in lower Mesopotamia. Nor would assigning all four kings as Assyrian kings as at least one researcher has proposed. This writer considers the Gutians – to the direct north of Elam and northeast of Shinar – as the fourth power in the alliance. We will look at the Gutium in more detail when we study Shem’s fifth son Aram in Chapter XXIII Aram & Tyre: Spain, Portugal & Brazil.
The three main regions for Shem’s children in Mesopotamia were the city-states of Assyria, then the Land of Shinar and thirdly, Elam. As we have learned, the land of Shinar was split into north and south – refer Chapter XVI Shem Occidentalis.
The North was known as Akkad – Akkadia or Accadia – and in time as Babylonia after its main city Babel; while the South was understood as Sumer. These two regions within Shinar, were the combined offspring of Shem’s son Arphaxad** – Chapter XXIV Arphaxad & Joktan: Balts, Slavs & the Balkans.
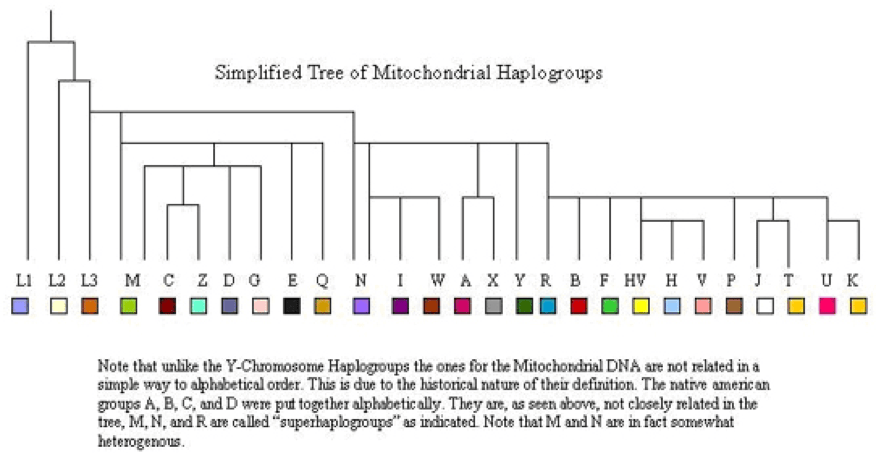
Arphaxad had two great grandsons, Peleg and Joktan. These two sons of Eber were the forefathers of a major split in the family line which we will study – and are confirmed in the Y-DNA super sub-Haplogroup split of R1 into the predominantly eastern R1a and western R1b. As an aside, the four remaining sons of Shem, while encompassing the earlier Haplogroups of G, I1 and I2 are principally identified by the paternal marker Haplogroups R1a and R1b.
There is good reason to acknowledge Peleg’s descendants comprised the northern territory of Akkad and Joktan’s children were located in Sumer. This would explain why two separate, yet closely related cultures arose though still under the banner of the Land of Shinar. Today, the same scenario has occurred with two distinct, yet adjacent regions of eastern and western nations within Europe – yet all descended from Arphaxad.**
In the British Museum there are artefacts mentioning three of the four northern kings at the Battle of the Valley of Siddim. The first two accounts record Chedorlaomer leading a rebellion with Tidal and Arioch’s son Dursrilani, a co-regent perhaps, against the king of Shinar at Babel circa 1929 to 1909 BCE, prior to the Valley of Siddim battle in 1894 BCE. The unnamed king of Shinar then strikes back. This king would have been from the Amorite Dynasty, the same as Hammurabi, the 6th king.
The two possible kings are the 4th king, Apil-Sin who reigned from 1930 to 1913 BCE or the 5th king, Sin-Muballit* from 1913 to 1894 BCE. Each are viable as Apil-Sin is Hammurabi’s grandfather and Sin-Muballit, his father. A clear and reasonable motive for Hammurabi’s later actions against Chedorlaomer, suddenly becomes apparent: revenge.
The first artefact is British Museum #BM 35404 – sp II.987, which says:
“The property and thepossessions of Babylon, small and great, in their faithful counsel to Chedorlaomer [Ku-der-lah-ga-mal], king of the land of Elam”… I am a King, the son of a king… the son of a daughter of the king who on the throne of dominion have sat…Dur-sir-ilani the son of Arioch [Eri-ekua] who with the spoil of the throne of dominion sat, and with the sword was killed.”
The second artefact is British Museum #BM 34062 – sp.158 & SPII.962 and states that Chedorlaomer the king of the Elamites, turned against the king of Shinar and attacked his cities at Babil and Borsippa:
“The enemy, the Elamite, multiplied evils against Bel [Baal] and Babil [Babel] which he planned evil against… there he set his mind on destroying the temple… the enemy, the Elamite, took itsgoods… He decreed it’s destruction… he showed his dislike for and barred the people of Bel of Ezida… the road to Sumer. Who is this Chedorlaomer [Ku-der-lah-ga-mal], the maker of this evil?
He has also gathered the Unman-Manda, and the people of Bel he has ruined… the Elamite caused his yoke to be directed down to Borsippa. He set his face against and he traversed also the road of darkness, the road to Mesku. This wicked man the Elamite, destroyed its palace, the princes he subdued with the sword, and from all the temples he carried off their goods as spoils of war, and he took them back to Elam.”
Notice Babylon is referred to as its original name of Babel – its name inherited prior to the Tower of Babel incident – Article: The Pyramid Perplexity.
Chedorlaomer was a formidable opponent, a ‘wicked man’ who had subdued a future threat in Babylon and with it, their king – either Hammurabi’s father or grandfather – before amalgamating the states into a powerful coalition.
Abraham and Chedorlaomer Chronological, Historical and Archaeological Evidence, Gérard Gertoux:
‘The Spartoli tablets (c. 650 BCE) describe [the] famous attack of Babylonia by a coalition of evil kings named Kudur-KUKUmal, [ku.ku means: carrying no mercy] king of Elam, Tudhula, king of Gutium, and Eri-Aku [king of Larsa].
This coalition of kings (Sumer, Larsa, Gutium) united under Kutur-Lagamar is quite likely, because all these kings were vassals or allies of the king of Elam (and Akkad) at that time, moreover, they came from neighbouring regions. Chedorlaomer’s route and the description of his actions show that this king came to this region near Egypt in order to maintain control over this new land trade route.
This ambitious project had to have worried Amenemhat I (1975-1946) because southern Canaan was a big source of supply. In order to protect Egypt, Amenemhat I built the “Walls of the Ruler”. One can notice that the area of Sodom is called Sutu(m) in execration texts (then Moab after 1800 BCE)’ Moab as a son of Lot, lived where Lot had previously dwelt.
Gertoux:
‘Thus the kings of Sumer [Ur] were oppressed on two occasions: once by Kudu [Lagamar in 1909 BCE]* king of Awan, and once by Kindadu [in 1882 BCE], king of Simaski. These two kings of Elam left a bad unforgettable memory in Sumerian annals. After the destruction of Ur the kings of Elam were blackened because they were charged with all misfortunes that occurred in the land of Sumer.’
The Pharaoh mentioned by Gertoux, Amenemhat I – who reigned from 1677 to 1647 BCE – was actually a Pharaoh while Joseph and the other sons of Jacob were dwelling in Goshen, the Nile delta region in Lower Egypt – some three hundred years after Gertoux’s orthodox, though inaccurate dating – Appendix IV: An Unconventional Chronology; and Appendix VII: Moses, the Exodus & the Red Sea Crossing – Fabrication or Fact?
The wall he built was to the east of the delta region, to protect the eastern Egyptian frontier from the inhabitants of the Sinai Peninsula. As relations with the Israelites were still favourable at this time, it would seem a benevolent act and not an insidious one to contain the prospering sons of Jacob within Egypt’s boundary; though this cannot be ruled out as a partial motive.
There is only one possible Pharaoh who ruled between 1929 BCE – the ascension of Chedorlaomer to the Elamite throne – and 1907 BCE, the first year of enforced tribute of the Transjordan City-States, who would have been concerned with the growing strength of Chedorlaomer.
The 3rd Pharaoh of the 1st Dynasty Djer, was the the son of Hor-Aha. Prominent during Djer’s reign was his grandmother, Queen Neithhotep. Cemetery evidence confirms that she lived during the reign of Hor-Aha and succeeded him into Djer’s rule. Neithoptep had been the wife of the 1st Pharaoh, Narmer also known as Menes. The First Dynasty of Egypt is incorrectly dated as beginning circa 3100 BCE. We will return to the dating and accurate sequencing of the Egyptian dynasties in an unconventional chronology.
Djer ruled Lower and Upper Egypt beginning 1922 BCE for fifty-four years until 1868 BCE. What is interesting about this Pharaoh is that it was Djer, who met Abraham and Sarah in 1902 BCE, during the 20th year of his reign while there was a famine in Canaan. We will return to this story in Genesis chapter twelve, when we study Abraham in Chapter XXVII Abraham & Keturah – Benelux & Scandinavia.
The third artifact is British Museum #BM 35496 – sp III.2. A new King of Shinar, namely Hammurabi – or Amraphel – counter-attacks Dursirilani, Tidal and Chedorlaomer:
“Samas [Babylonian sun god] the illuminator of… Merodach [chief Babylonian god]… the rulers who were not nourishing… he caused to be slain. Dur-sir-ilani, the son of Arioch [Eri-ekua]… his goods he carried off to the waters of Babylon and back to the temple of Esaggil… his son, with the weapon of his hands, like a lamb he was slaughtered… the child he cut off… Tidal [Tu-ud-hul-amar] son of Gazza… his goods he carried off to the waters of Babylon and to the temple of Esaggil…
His son, with the weapon of his hands, fell upon him… of his dominion, before the temple of Annunit… Elam, the city of Ahhe to the land of Rabbatu, he spoiled in ruins, he set the fortress of Akkad, the whole of Borsippa…ended Chedorlaomer [Ku-der-lah-ga-mal], his son, and with the steel sword he pierced his heart… his enemy. He took the will of these kings, the lords of sin… their rebellions… who the chief of the gods, Merodach, brought his anger against.”
It entailed a series of battles over a number of years imposed by the king of Shinar, violently slaughtering the other three kings and their families and in the process… ending three separate dynasties in a bloodbath of destruction. The artefacts confirm the names of Dursirilani, Tidal, and Chedorlaomer. Possibly, Arioch was the one casualty amongst the Mesopotamian kings during Abraham’s night time raid and this is why his son Dursirilani is listed as king of Ellasar (or Larsa), at the time of Hammurabi’s betrayal and revenge. Alternatively, Dursirilani may have been a co-regent with his father Arioch.
It was shortly after the Battle of the Valley of Siddim, when Hammurabi rebelled and slaughtered his – once allies now – enemies, beginning in 1893 BCE.
It may now explain why Amraphel is listed first in the Genesis account. Ultimately, he killed his three rivals; each powerful rulers in southern Mesopotamia. As the king of Babylon and Akkad, Amraphel added the kingship of Sumer while subjugating both the lands of Elam and the Guti.
Regarding Chedorlaomer, the International Standard Bible Encyclopaedia, on British Museum Sp. II 987 and Sp. III, 2, records:
‘… refers to the bond of heaven extended to the four regions, and the fame which Merodach set for the Elamites in Babylon, the city of his glory. So the gods, in their faithful or everlasting counsel, decreed to Kudur-lahgumal, king of Elam theirfavor. He came down, and performed what was good to them, and exercised dominion in Babylon, the city of Kar-Dunias (Babylonia). When in power, however, he acted in a way which did not please the Babylonians… [between 1929 and 1894 BCE].
The less perfect fragment (Sp. III, 2) contains, near the beginning, the word hammu, and if this be, as Professor F. Hommel has suggested, part of the name Hammurabi (Amraphel), it would in all probability place the identification of Kudur-lahgumal with Chedorlaomer beyond a doubt.’
This would cement an already compelling argument for the veracity of the king of Shinar’s identity as Hammurabi, who as Amraphel, was a contemporary of and briefly allied with Chedorlaomer, when he ascended the throne in 1894 BCE. Amraphel then in turn, rebelled against Chedorlaomer, killing him in 1893 BCE for the humiliation perpetrated against probably his father, Sin-Muballit or possibly his grandfather, Apil-Sin.

King Hammurabi
Hammurabi and the Babylonian Empire, Dr Joshua J Mark, 2018 – emphasis mine:
‘Hammurabi (also known as Khammurabi and Ammurapi… assumed the throne… and expanded the kingdom to conquer all of ancient Mesopotamia. The kingdom of Babylon comprised only the cities of Babylon, Kish, Sippar, and Borsippa when Hammurabi came to the throne but, through a succession of military campaigns, careful alliances made and broken when necessary, and political manoeuvres, he held the entire region under Babylonian control by [his death].
According to his own inscriptions, letters and administrative documents from his reign, he sought to improve the lives of those who lived under his rule. He is best known in the modern day for his law code which, although not the earliest code of laws, came to serve as a model for other cultures and is thought to have influenced the laws set down by Hebrew scribes, including those from the biblical Book of Exodus.
The fifth king of the dynasty, Sin-Muballit… successfully completed many public works projects but was unable to expand the kingdom or compete with the rival city of Larsa to the south. Larsa was the most lucrative trade center on the Persian Gulf and the profits from this trade enriched the city and encouraged expansion so that most of the cities of the south were under Larsa’s control.
Sin-Muballit [1913-1894 BCE] led a force against Larsa but was defeated by their king Rim Sin I[1924-1865 BCE]. At this point it is uncertain what exactly happened, but it seems that Sin-Muballit was compelled to abdicate in favor of his son Hammurabi. Whether Rim Sin I thought Hammurabi would be less of a threat to Larsa is also unknown but, if so, he would be proven wrong.
The historian Durant writes:
“At the outset of [Babylonian history] stands the powerful figure of Hammurabi,conqueror and lawgiver through a reign of forty-three years. Primeval seals and inscriptions transmit him to us partially – a youth full of fire and genius, a very whirlwind in battle [akin to Alexander the Great], who crushes all rebels, cuts his enemies into pieces, marches over inaccessible mountains, and never loses an engagement. Under him the petty warring states of the lower valley were forced into unity and peace, and disciplined into order and security by an historic code of laws.”
‘The alliances [Hammurabi] made with other states would repeatedly be broken when the king found it necessary to do so but, as rulers continued to enter into pacts with Hammurabi, it does not seem to have occurred to any of them that he would do the same to them as he had previously to others. A technique he seems to have used first in this engagement would become his preferred method in others when circumstances allowed: the damming up of water sources to the city to withhold them from the enemy until surrender or, possibly, withholding the waters through a dam and then releasing them to flood the city before then mounting an attack.’
In 1866 BCE, the undefeated Hammurabi turned against Rim-Sin I because he had refused to support Hammurabi in his ongoing war against Elam, despite pledging troops. Hammurabi with extra troops from Mari, attacked Mashkan-shapir located on the northern edge of Rim-Sin’s realm. Hammurabi’s forces reached Larsa with alacrity and after a six-month siege the city of Larsa fell. Rim-Sin I escaped from the city but was soon found, taken prisoner and died thereafter in 1865 BCE. Rim-Sin I was the 14th and last king of the Larsa Dynasty which had begun in 2128 BCE.
In 1864 BCE, Hammurabi defeated a coalition that stood against him comprising Elam, the Guti and the Marhashi kingdom in Iran. The following year, he defeated Zimri-Lim the King of Mari, an Amorite kingdom northwest of Babylon and his former ally. Hammurabi not only broke his alliance with Zimri-Lim but also for the first and only time, completely destroyed Mari rather than conquering it. Hammurabi would subdue cities, absorb them into his kingdom, repair and improve them. Scholars have debated his reasons and believe Mari’s great wealth posed a threat and was too close in proximity to Babylon’s designs on being the greatest city in Mesopotamia.
After Mari’s destruction, Hammurabi marched on Asshur, took control of the extent of Assyria and then Eshunna; so that by 1857 BCE – five years before his death at age sixty – he ruled all of Mesopotamia.
Joshua Mark: ‘A popular title applied to Hammurabi in his lifetime was bani matim, ‘builder of the land’, because of the many building projects and canals he ordered constructed throughout the region. Documents from the time attest to the efficacy of Hammurabi’s rule and his sincere desire to improve the lives of the people of Mesopotamia… letters and administrative works… such as directives for the building of canals, food distribution, beautification and building projects, and legal issues…
His law code is not the first such code in history (though it is often called so) but is certainly the most famous from antiquity prior to the code set down in the biblical books. The Code of Ur-Nammu… which originated with either Ur-Nammu or his son Shulgi of Ur, is the oldest code of laws in the world. Unlike the earlier Code of Ur-Nammu, which imposed fines or penalties of land, Hammurabi’s code epitomized the principle known as Lex Talionis, the law of retributive justice, in which punishment corresponds directly to the crime, better known as the concept of ‘an eye for an eye and a tooth for a tooth’, made famous from the later law code of the Old Testament…
By [1857 BCE]… Hammurabi was old and sick. In the last years of his life his son, Samsu-Iluna’ who ruled from 1852 to 1815 BCE, ‘had already taken over the responsibilities of the throne and assumed full reign by’ 1851 BCE. ‘The conquest of Eshnunna had removed a barrier to the east that had buffered the region against incursions by people such as the Hittites and Kassites. Once that barrier was gone, and news of the great king weakening spread, the eastern tribes prepared their armies to invade.
The vast kingdom Hammurabi had built during his lifetime began to fall apart within a year of his death, and those cities that had been part of vassal states secured their borders and announced their autonomy. None of Hammurabi’s successors could put the kingdom back together again, and first the Hittites… then the Kassites invaded. The Hittites sacked Babylon and the Kassites inhabited and re-named it. The Elamites, who had been so completely defeated by Hammurabi decades before, invaded and carried off the stele of Hammurabi’s Law Code which was discovered at the Elamite city of Susa in 1902 CE.’

Gérard Gertoux summary:
‘Kedor-Lagomer corresponds to Kudur-Lagarma which is an Akkadian transcription of Kutir-Lagamal “bearer (servant) of Lagamal”. According to the biblical text (Genesis 10:10), Shinar was a region south of Mesopotamia composed of at least three major cities: Babylon (Babel), Uruk (Erech) and Aggad (Akkad). In time the name Babylon came to mean the whole of Babylonia (Daniel 1:2). During the period [1988-1894 BCE] the two main actors in the Mesopotamian world were the kings of Ur III and the kings of [late] Awan I [/II and early Shimashki].
The power of these two empires [Sumer and Elam] depended on trade and therefore control of trade routes. They earned money through vassal kings who levied customs duties on traders passing through their territories and had to pay to their “emperors” for ensuring their security (by means of military force). Kudur-Lagamar probably wanted to create a new major trade route from Susa to Egypt.
The route taken by Abraham andthat one followed by Chedorlaomer are in agreement with the major communication routes of the time.
In this context, the capture of the goddess Nanaya [in 1909 BCE] served to justify the westward expansionist projects of Kudur-Lagamar. Indeed, change in titulatures confirm his new role of “king of Akkad”. The complete titulature of the kings of Awan I, as the one of Puzur-Insusinak, was as follows: governor (ENSI) of Susa, viceroy (GIR.NITA) of Elam and king (LUGAL) of Awan.
Abram…at that time… lived in Ur… he must have learned that Chedorlaomer had confiscated the statue of the goddess Nanaya [Inana or Ishtar].
[As the Assyrian king] Ashurbanipal refers exactly [circa 660 BC] to Ku-du[r-Lagamar], king of Awan I, in Sumerian royal lists and as the Spartoli tablets describe the attack of Babylonia by the king of Elam named Kudur-KUKUmal, this king of Elam must have been Chedorlaomer.
Prior to [1909 BCE] relationships with the kings of Elam remained cordial… From this date Kutur-Lagamar behaves as “King of Akkad” and, in the same way as Sargon of Akkad, he chose to open a new trade route to the west as far as Egypt. Titulary of Ur… kings changed… [from] King of Sumer and Akkad… [to] King of the 4 corners (of Universe) [an indicative title of the later Mede and Persian (Elamite) empire], indicating that Akkad was no longer under full control of the king of Ur…
[In summation]: King Kudur-Lagamar [reigning from 1929 to 1893 BCE] alias Chedorlaomer, actually existed since he was the third and last king of Awan I, the only Elamite dynasty mentioned in Sumerian lists. His two main actions that have passed to posterity were the capture of Uruk’s goddess (Nanaya) and [the] looting of the city of Sodom.’
The timing of two years – as deduced from Gertoux’s chronology – prior to the beginning of the tribute being exacted on the Canaanite cities in 1907 BCE, means King Chedorlaomer of Elam with his allies, Tudhula, king of the Gutium, and Eri-Aku king of Larsa, would have fought both the kings of Babylon [Akkad] and Sumer [Uruk] to gain control of the land of Shinar. This was twenty years after Chedorlaomer came to the throne of Elam and thus gave him ample time to consolidate his power, build his military capability and win or subjugate the necessary allies.
This means, we now know which king he fought against in Babel; it would have been Hammurabi’s father, Sin-Muballit who reigned from 1913 to 1894 BCE – the 5th king of the Amorite Babylonian Dynasty – and in Ur, King Shu-Suen ruler from 1915 to 1906 BCE; the grandson of Shulgi, the son of Ur-Nammu, the founder of the Ur III Dynasty. This explains the abdication of Sin-Muballit in favour of his son, Hammurabi who was probably chosen by Chedorlaomer as a puppet king. A role that the young Amraphel spectacularly did not follow.
Hasting’s Dictionary of the Bible, C H W Johns & James Hastings, 1909:
‘Arioch king of Ellasar was allied with Chedorlaomer in the campaign against the kings of the plain (Genesis 14:1). He has been identified with Rim-sin, king of Larsa, and consequently Ellasar is thought to be for al-Larsa, the city of Larsa. Larsa, modern Senkereh in Lower Babylonia on the east bank of the Euphrates, was celebrated for its temple and worship of the sun-god Shamash’ – Article: Monoliths of the Nephilim.
The meaning of Ellasar is very close to the meaning of Nimrod, who we will study in detail – Chapter XXI The Incredible Identity, Origin & Destiny of Nimrod.
Ellasar in Hebrew means ‘rebellious God’ or ‘onto rebellion’ from the word ‘el, meaning God; or denoting motion toward and the verb sarar, ‘to be rebellious’ or ‘stubborn’, though more in attitude rather than revolt.
The city of Ellasar, is believed by most scholars to be the same city identified as Larsa. Some place it far north where the Hurrians dwelt, though this would not fit with the cluster of the remaining three cities in southern Mesopotamia. Larsa is credibly located southeast of the very ancient city of Erech or Uruk – from which Iraq derives its name – and northwest of Ur, where Abraham’s family originated – Chapter XXV Italy: Nahor & the Chaldeans.
Tudhula of the Gutium is reputed to have ruled approximately from 1909 to either 1893 or possibly 1864 BCE. Support for these dates, is that Tidal may have come to power due to Chedorlaomer’s politicking and thus as one of his allies, would have assisted in the defeat of Babylon and Ur in 1909 BCE. Plus, Tidal if still king, would have died when Hammurabi defeated his coalition with Elam in 1864 BCE – or more likely earlier in 1893 BCE as discussed.
International Standard Bible Encyclopedia – emphasis mine:
‘ERI-AKU er-i-a-koo’, e-ri-a-ku’: This is the probable Sumerian reading of the well-known Babylonian name written with the characters for “servant” (Sem wardu or ardu) and the group standing for the Moon-god Sin^ (written En-zu = Zu-en), otherwise Aku, the whole meaning “servant of the Moon-god.” This ruler, who was king of Larsa [Ellasa], is generally identified with the Arioch of Genesis 14:9. Eri-Aku belonged to an Elamite family which held the throne of Larsa, a state which, in common with Babylonia itself, acknowledged the suzerainty of Elam… it may be noted, that the expression adda, “father,” probably means simply “administrator”.’
Gérard Gertoux:
‘The Akkadian name Warad-Sin, king (LUGAL) of Larsa, is written Eri-Aku (e-ri-a-ku) which is a transcription of the Sumerian name IR-AGA “servant of the lunar disc” translated into Akkadian as (u)-ar-du-a-gu… Warad-Agu, an equivalent of Warad-Sin “servant of the Moon^ (god)”.’
What is interesting here, is that Rim-Sin I was the final king of the Larsa Dynasty from 1924 BCE to 1865 BCE and he is identified with Arioch of Ellasar (or Eri-Aku of Larsa). Yet Gertoux says Warad-Sin is also Eri-Aku, or Arioch. In the king lists, Warad-Sin was the brother of Rim-Sin I and supposedly ruled for twelve years prior to his brother from 1936 BCE to 1924 BCE and as a co-regency with his father, Kudur-Marbuk. Arioch, may then be a family name, a title, or even a descriptive name.
For we learn more about Eri-Aku in the Targum of Palestine account of Genesis 14:9, in that Eri-Aku was a giant. He was called Arioch due to his great height. Arioch is derived from Arik which means ‘tall among the giants’. Even compared to other giants, Arioch was impressive and intimidating. This is an interesting piece of information, as the Northern confederacy fought against Nephilim descended Elioud giants before literally turning around to subdue the five Canaanite kings.
Picking up the story from Genesis Six Giants, emphasis mine:
‘Of course, no ancient records exist that tell us how many giants served under Chedorlaomer. He may have had only Arioch, or that towering king plus a few others, or he may have had many such men in his service. In any event, the results of their opening battle with the Jordanian giants clearly show that he commanded a far superior force. Sweeping down the valley, his army quickly laid siege to Ashteroth Karnaim.
This chief city of the Rephaim lay in the district of Bashan,’ – refer Chapter XXII Alpha & Omega; and Chapter XXXIV Dan: The Invisible Tribe – ‘about six miles northwest of Edrei. These giants worshipped Astarte, the goddess of the crested^ moon’ – refer article: Lilith.
‘They were greatly decimated. Continuing along what the ancients called the King’s Highway, a trade route that ran the entire length of the Trans-jordanian plateau to the Gulf of Aqabah, Chedorlaomer and his confederate kings next fell upon the enormous Zamzummim people at Ham. Some archaeologists identify this city with modern Ham, which is located in eastern Gilead, about four miles south of Irbid.
After this, the kings from Elam and Mesopotamia attacked and cut off the terrible Emim giants at nearby Shaveh Kiriathaim. These people, described as “great and many and tall,”occupied the land that the Moabites later took. Sodom and Gomorrah, at the [northern] tip of the Salt Sea, stood next in line. They quickly got ready to defend themselves, expecting the worst. But to their amazement the invaders passed them by. Pressing on southward into the rough mountain range of Seir, Chedorlaomer waged war instead against the giant Horites.’
The land of Canaan was infested with Nephilim descended Elioud and was literally the land of the giants. In verse seven of Genesis chapter fourteen, just after the Horites are mentioned, we read about the defeated Amalekites. This reveals that the Amalekites existed before Esau had a future grandson called Amalek, some one hundred and twenty years later. Esau was to marry into and live with the Nephilim related Horites.
The Amalekites of the Bible are identifiable in secular sources under a different name, which we will study. The link in Genesis fourteen between the Horites and Amalek and then Esau marrying into the Horites and naming a grandson Amalek is not only not a coincidence, but rather quite significant. The Amalekites were also Elioud and related to the giant Horites – refer Chapter XXIX Esau: The Thirteenth Tribe; and article: Na’amah.
Genesis 6 Giants:
‘He also conquered the Negev to eliminate any threat from that quarter. Having thus neutralized all the countryround, he finally turned hisattention upon the rebellious Sodom and Gomorrah and their neighbors. Giving up whatever security their fortified walls afforded them, “the king of Sodom and the king of Gomorrah and the king of Admah and the king of Zeboiim and the king of Bela (that is, Zoar) came out,” notes Moses; “and they arrayed for battle against them in the valley of Siddim, against Chedorlaomer king of Elam and Tidal king of Goiim and Amraphel king of Shinar and Arioch king of Ellasar – four kings against five.”
Regarding these ‘Canaanites’, the Book of Jasher 10:25-27, states:
‘And four men from the family of Ham went to the land of the plain; these are the names of the four men, Sodom, Gomorrah, Admah and Zeboyim. And these men built themselves four cities in the land of the plain, and they called the names of their cities after their own names. And they and their children and all belonging to them dwelt in those cities, and they were fruitful and multiplied greatly and dwelt peaceably.’
Recall, the original inhabitants of Canaan unsurprisingly, were the peoples descended from Canaan – the half-brother of Ham – refer Chapter XI Ham Aequator.
The Nephilim arrived after the Canaanites and dwelt amongst them. The Book of Jasher claims Nimrod was the king of Shinar. We have learned that Hammurabi is undoubtedly the king in question. Nearly 5,000 years elapsed since Nimrod and the Tower of Babel incident and though longevity was on his side, it would be unlikely he was still living at this time. Such a powerful figure such as he was, he would have been still ruling and making his presence known if alive. His inferred demise points to when the Tower was ‘destroyed’ – refer Chapter XXI The Incredible Identity, Origin & Destiny of Nimrod.
Genesis 6 Giants:
‘This bold strategy to meet the invaders in the open field was decided by the surrounding treacherous terrain. Many slime pits, dug to obtain pitch or mortar for building, transversed the area. While most English translations simply describe the Valley of Siddim as being “full of slime pits,” the force of the original Hebrew language, according to Speiser, conveys to the reader a picture of “one bitumen pit after another.” The locals were most familiar with the locations of these pits. The invaders were not.
They were also accustomed to the foul-smelling, boiling waters on whose surface floated lumps of asphalt or bitumen the size of bulls. The enemy, they hoped, would be at least a little disconcerted by the unfamiliar terrain and terrible odor and afraid of falling into the boiling waters. But the pits failed to deter the invaders. Indeed, they soon turned them to their own advantage. In the resulting warfare, many in the defenders’ ranks saw death.
Alarmed by the way the battle was progressing against them, the five local kings and their armies panicked and attempted to flee the field. The slime pits, however, made retreat difficult. In the confusion, two of the fleeing kings – and presumedly many men with them – fell into the tar pits. Those who escaped fled into the mountains.
For a time some scholars disbelieved this Genesis story, labeling it a fiction. But evidence dug up by archaeologists in recent years verifies that in Abraham’s time a great destruction came upon the very places mentioned in Chedorlaomer’s invasion.
Dr. Nelson Glueck, whose work in this area extended from 1932 until 1947, when it was halted by the Israeli-Arab disturbances, reports that the highly developed civilization which flourished here during the Middle Bronze I period (c. 2100-1900 B.C.) came to an abrupt and savage end [in 1894 BCE].
This well-known archaeologist found that not only the cities mentioned in Genesis but also many villages – beginning with Ashtaroth-Karnaim and proceeding south through Transjordan and the Negev to Kadesh Barnea in the Sinai – were systematically gutted. “From southern Syria to central Sinai, their fury raged,” he writes.
“A punitive expedition developed into an orgy of annihilation. I found that every village in their path had been plundered and left in ruins, and the countryside laid waste. The population had been wiped out or led away into captivity. For hundreds of years thereafter, the entire area was like an abandoned cemetery, hideously unkept, with all its monuments shattered and strewn in pieces on the ground.”
Flying Serpents and Dragons, R A Boulay, 1997 & 1999, Page 148:
‘The power of the invading kings, numbered as 800,000 according to the Haggadah, must have been overwhelming indeed, for they not only crushed these fortified cities but they never were rebuilt and the land [of the northern tip of the Dead Sea] remained unoccupied for a thousand years.’
Some will repeatedly take an opposing view and there will always be those who do not see what is in plain sight. Yet we have substantial verification documenting as historically authentic, the biblical account recording a devastating war.
The four northern kings were real personages and led the ancient coalition comprising city-states located in Elam, Akkad, Sumer and Aram. Acadia represented by descendants of Peleg and Sumer by those from Joktan – brothers and great grandsons from Shem’s son Arphaxad, collectively known as the land of Shinar – and with Elam and Aram, they exacted terrible revenge for disobedience by the southern kings of Ham and the Nephilim descended Elioud giants.
The modus operandi consisting of devastating destruction rings true, for we have learned how both Chedorlaomer and Hammurabi were uncompromising in their style of warfare. Possibly, a further reason why Amraphel is listed first, even while still a youngster; with his blitzkrieg style, he likely made a sizeable impression and perhaps shared the lead in the ensuing carnage; the obliteration of the opposition forces; and the desolation of their land.
“Look,” says the Teacher, “I have discovered this by adding one thing to another to find out the explanation…”
Ecclesiastes 7:27 Christian Standard Bible
“I would rather be in minority and be right, than in the majority and wrong.”
Jodi Picoult
© Orion Gold 2020 – All rights reserved. Permission to copy, use or distribute, if acknowledgement of the original authorship is attributed to orion-gold.com